05-06-2024 19:55
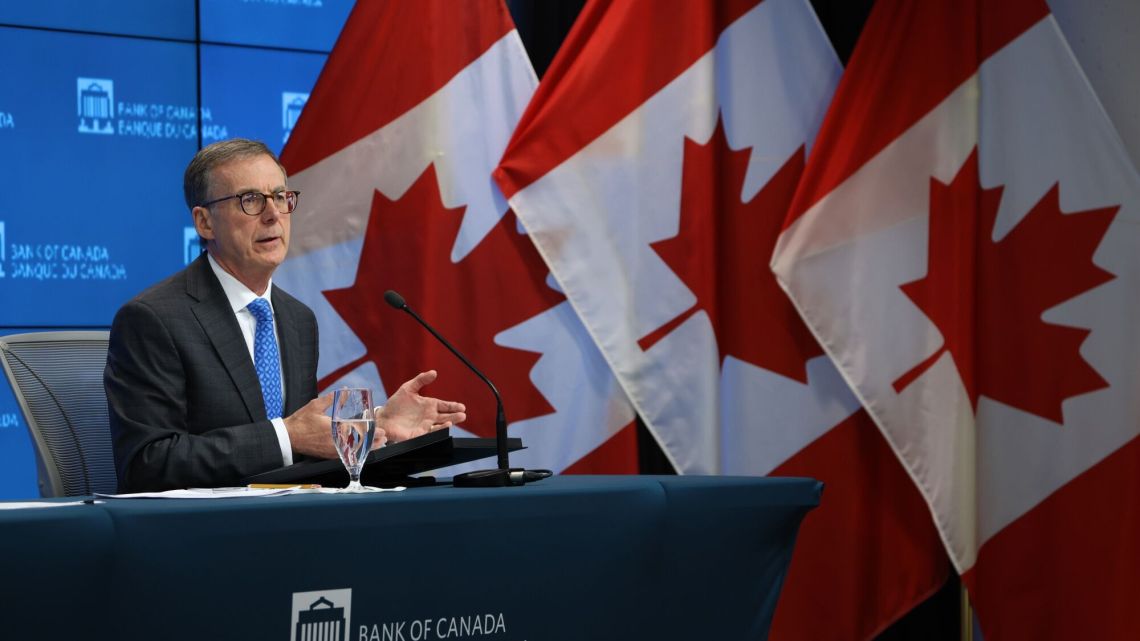
He Bank of Canada cuts interest rates by a quarter of a percentage pointl, becoming the first central bank in the Group of Seven to begin an easing cycle.
Monetary policy makers, led by the governor Tiff Macklemcut the benchmark overnight interest rate on Wednesday 4.75%as expected by markets and economists in a Bloomberg survey. The authorities are more convinced that inflation on the way to the 2% objectiveand they claim that it is “it is reasonable to expect further reductions» if progress continues.
For the Bank of Japan, it is possible to increase interest rates after the rule changes
Authoritarians don't like it
The practice of professional and critical journalism is a fundamental pillar of democracy. This is why it bothers those who believe they have the truth.
Canada: the reason for the rate cut
“With growing evidence of a slowdown in underlying inflation, monetary policy no longer needs to be so restrictiveMacklem said in prepared remarks.
Canadian bonds rose after the decline. The Canadian government's 2-year bond rate fell 5.9 basis points at 10:10 a.m. Ottawa time. The Canadian dollar depreciated to 1.3729 per US dollar.
The bank said the path to easing will depend on the rise in inflation, which “is likely to be uneven.” Potential risks to the outlook include global tensions, a faster-than-expected rise in house prices and strong wage growth relative to productivity.
“We don't want monetary policy to be more restrictive than necessary to bring inflation back to its target. But if we lower our policy rate too quickly, we could jeopardize the progress we have made,” Macklem said.
This is the Bank of Canada's first rate cut since 2020. The bank thus shows that it is increasingly confident that it is on the verge of declaring victory over inflation, which fell at an annual rate of 2.7% after peaking in mid-2022, this allows interest rates to begin to normalize after one of the most aggressive hiking cycles in central bank history.
“It only took the central bank 11 months to go from increases to cutsbut this cycle is very different. In fact, the official interest rate has this time reached much more restrictive levels than those observed in recent decades,” writes Royce Mendes, general manager of Desjardins Securities, in a report.
There is, however, uncertainty over how quickly borrowing costs will fall. In addition to the risks to the inflation outlook, The Bank of Canada beats the Federal Reserve. Historically, interest rates in both countries have tended to follow a similar trajectory, and when this is not the case, some pressure is put on the currency. A weak Canadian dollar means higher import costs, with a risk of higher inflation. Macklem said there were limits to differences between his central bank and its U.S. counterpart.
The Bank of Canada's reduction decision This comes a day before the European Central Bank does the samemaking it the first in the G7 to begin a flexibility cycle. Canada's central bank has joined the Swiss National Bank and Sweden's Riksbank in adopting a more expansionary policy as inflation risks ease.

“Amateur introvert. Pop culture trailblazer. Incurable bacon aficionado.”